The Science Behind Coffee Roasting
Discover the chemical reactions and flavor development that occur during the art of coffee roasting.
Introduction to Coffee Roasting
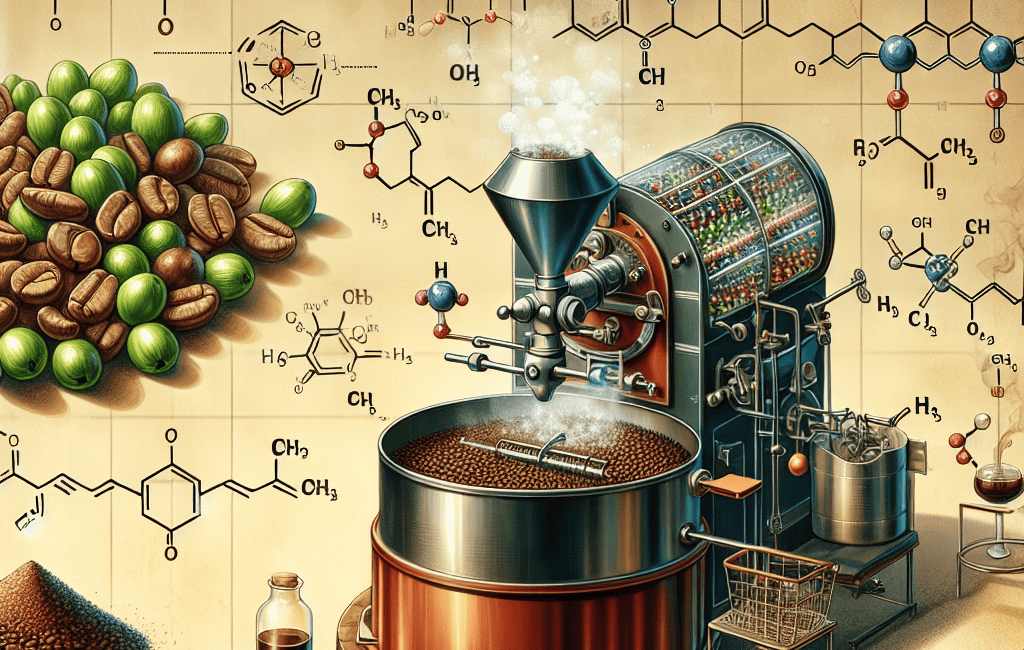
Coffee roasting is more than just a cooking process; it’s a fascinating transformation that occurs when green coffee beans are subjected to heat. The roasting process not only changes the color and size of the beans but also unlocks a myriad of flavors and aromas. Let’s delve into the science behind this transformation!
The Roasting Process
When coffee beans are roasted, they undergo several physical and chemical changes. Here are the key stages:
- Drying Phase: The initial stage where moisture evaporates from the beans.
- Maillard Reaction: A complex reaction between sugars and amino acids that begins to develop flavor and color.
- Caramelization: Sugars begin to caramelize, adding sweetness and depth to the flavor profile.
- First Crack: A rapid expansion of gases that produces a popping sound as the beans release moisture, indicating the transition to a light roast.
- Development Phase: The time after the first crack where flavors continue to develop based on the roast duration.
- Second Crack: A more subtle crack indicating a darker roast, where oils surface and flavors intensify.
Chemical Reactions During Roasting
Several key chemical reactions contribute to the development of flavors during roasting:
- Maillard Reaction: This reaction creates hundreds of flavor compounds, contributing to the rich, complex flavors we associate with roasted coffee.
- Pyrolysis: The breaking down of organic material when exposed to heat, leading to the formation of aromatic compounds.
- Oxidation: Some compounds oxidize during roasting, enhancing flavors but can also lead to rancidity if coffee is stored improperly.
Understanding these reactions allows roasters to manipulate the roasting time and temperature to achieve desired flavor profiles.
Flavor Development
The balance of acidity, sweetness, bitterness, and body in coffee is influenced by the roasting process. Here‘s how:
- Light Roasts: Preserve the original flavors of the coffee bean, highlighting fruity and floral notes.
- Medium Roasts: Strike a balance between acidity and sweetness, often bringing out nutty and caramel flavors.
- Dark Roasts: Emphasize bitterness and deep chocolate flavors, often with smoky undertones.
Each roast level creates a unique sensory experience, making coffee tasting a delightful adventure.
Conclusion
Understanding the science behind coffee roasting enriches our appreciation for this beloved beverage. The combination of chemical reactions and the skill of the roaster creates a complex tapestry of flavors, making each cup of coffee a unique experience.
Whether you prefer a light, fruity brew or a bold, dark roast, every sip tells the story of its journey from bean to cup.