The Economics of Coffee: From Bean to Barista
Coffee is more than just a beverage; it’s a global industry that fuels economies, shapes cultures, and ignites passions. From the moment a coffee bean is harvested to the time it reaches your cup, a complex economic journey unfolds. Let‘s explore this fascinating process!
The Coffee Supply Chain
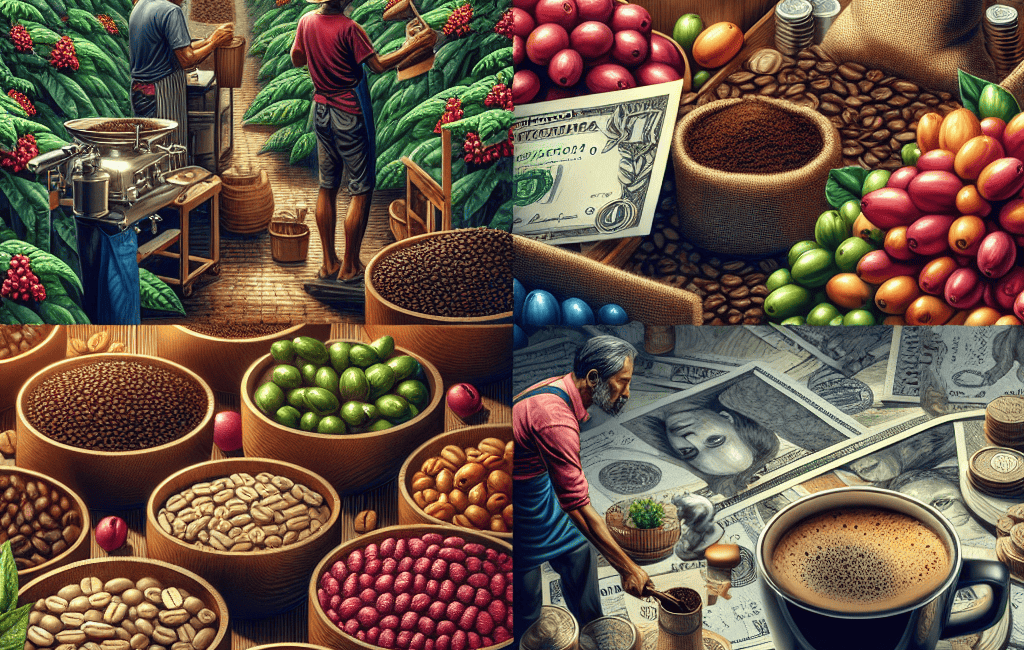
The journey of coffee begins on the farms where it is grown. The supply chain can be broken down into several stages:
- Farming: Coffee is primarily grown in tropical regions around the world, commonly referred to as the “Coffee Belt.” Countries like Brazil, Vietnam, Colombia, and Ethiopia lead in coffee production.
- Processing: Once harvested, coffee cherries undergo processing to extract the beans. This can be done through various methods, such as the wet or dry process.
- Exporting: After processing, beans are exported to different countries, where they often go through another round of quality control before reaching roasters.
- Roasting: Roasters play a vital role in developing the flavor profile of coffee. This stage can significantly affect the final price of the product based on the quality of the beans and the roasting process used.
- Brewing: Finally, the coffee reaches cafes and consumers. Baristas craft drinks that not only delight the palate but also showcase the unique characteristics of the beans.
The Economic Impact
Coffee is one of the most traded commodities in the world. Its economic impact is substantial:
- Employment: Millions of people are employed in the coffee industry, from farmers to baristas. In developing countries, coffee farming is often a primary source of income.
- Trade: Coffee is a key export for many countries, contributing significantly to their GDP. The global coffee market is estimated to be worth over $100 billion.
- Sustainability: As demand for ethically sourced coffee grows, more producers are adopting sustainable practices. This shift can help improve the livelihoods of farmers and contribute to environmental conservation.
Trends in Coffee Economics
The coffee industry is constantly evolving, with several trends shaping its future:
- Specialty Coffee: Consumers are increasingly seeking high-quality, unique coffee experiences. This trend drives higher prices for specialty beans, benefitting farmers who invest in quality.
- Direct Trade: More roasters are establishing direct relationships with farmers, promoting transparency and fair pricing, which in turn supports sustainable farming practices.
- Technology: Innovations in brewing equipment and online sales platforms are changing how coffee is consumed and marketed, making it more accessible to consumers worldwide.
Conclusion
The economics of coffee is a complex and dynamic field that reflects broader trends in global trade, consumer behavior, and sustainable practices. As you sip your next cup of coffee, remember the journey it took to reach you—from bean to barista. Embracing this knowledge not only enhances your appreciation for the beverage but also supports a thriving global community.